จุดศูนย์ถ่วง: นี่คือโพสต์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับหัวข้อนี้
The center of gravity is a geometric property of any object.
The center of gravity is the average location of the
weight
of an object. We can completely describe the
motion
of any object through space in terms of the translation of
the center of gravity of the object from one place to another, and
the rotation of the object about its center of gravity if it
is free to rotate. If the object is confined to rotate about some
other point, like a hinge, we can still describe its motion.
In flight, both
airplanes
and
rockets
rotate about their centers of gravity.
A kite, on the other hand, rotates about the
bridle point.
But the
trim
of a kite still depends on the location of the
center of gravity
relative to the bridle point, because for every object the weight always acts through the
center of gravity.
Determining the center of gravity is very important
for any flying object.
How do engineers determine the location of the center of
gravity for an aircraft which they are designing?
In general, determining the center of gravity (cg) is a complicated
procedure because the mass (and weight) may not be uniformly distributed
throughout the object. The general case requires the use of calculus
which we will discuss at the bottom of this page.
If the mass is uniformly distributed, the problem is greatly simplified.
If the object has a line (or plane) of symmetry, the cg lies
on the line of symmetry.
For a
solid block of uniform material, the center of gravity is simply
at the average location of the
physical dimensions. (For a rectangular block, 50 X 20 X 10,
the center of gravity is at the point (25,10, 5) ).
For a triangle of height h, the cg is at h/3, and for a semi-circle of radius
r, the cg is at (4*r/(3*pi)) where pi is ratio of the circumference of the
circle to the diameter. There are tables of the location of the center of gravity
for many simple shapes in math and science books. The tables were generated
by using the equation from calculus shown on the slide.
For a general shaped object, there is a simple mechanical way to
determine the center of gravity:
- If we just balance the object using
a string or an edge, the point at which the object
is balanced is the center of gravity. (Just like balancing a
pencil on your finger!) - Another, more complicated way, is a two step method shown on
the slide. In Step 1, you hang the object from any
point and you drop a weighted
string from the same point. Draw a line on the object along the
string. For Step 2, repeat the procedure from another point on the object
You now have two lines drawn on the object which intersect.
The center of gravity is the point where the lines intersect. This
procedure works well for irregularly shaped objects that are hard
to balance.
If the mass of the object is not uniformly distributed, we must use calculus
to determine center of gravity.
We will use the symbol S dw to denote the integration of a continuous
function with respect to weight. Then the center of gravity can be determined from:
cg * W = S x dw
where x is the distance from a reference line, dw is an
increment of weight, and
W is the total weight of the object.
To evaluate the right side, we have to determine how the weight varies
geometrically. From the
weight equation, we know that:
w = m * g
where m is the mass of the object, and g is the gravitational
constant. In turn, the mass m of any object is equal to the
density, rho,
of the object times the
volume, V:
m = rho * V
We can combine the last two equations:
w = g * rho * V
then
dw = g * rho * dV
dw = g * rho(x,y,z) * dx dy dz
If we have a functional form for the mass distribution, we can solve the
equation for the center of gravity:
cg * W = g * SSS x * rho(x,y,z) dx dy dz
where SSS indicates a triple integral over dx. dy. and dz.
If we don’t know the functional form of the mass distribution,
we can numerically integrate the equation using a spreadsheet.
Divide the distance into a number of small volume segments and
determining the average value of the weight/volume (density times gravity) over
that small segment. Taking the sum of the average value of the weight/volume
times the distance times the volume segment
divided by the weight will produce the center of gravity.
Activities:
Guided Tours
-
Aircraft Weight:
-
Fuselage:
Navigation ..
- Beginner’s Guide Home Page
Table of Contents
[Update] คำศัพท์ ”จุดศูนย์ถ่วง” แปลว่าอะไร? | จุดศูนย์ถ่วง – Australia.xemloibaihat
บริการเปิดพจนานุกรมอัตโนมัติ ติดโพย (PopThai)
บริการ ติดโพย (PopThai)
เป็นบริการเปิดพจนานุกรมอัตโนมัติ โดยผู้ใช้สามารถป้อนข้อความ ทีละประโยค หรือ เป็นหน้าเลยก็ได้ ไม่จำเป็นต้องทีละคำสองคำ
ระบบจะทำการแนบความหมายของคำหรือวลีภาษาต่างประเทศ
(ปัจจุบันสนับสนุน ภาษาอังกฤษ, ญี่ปุ่นและเยอรมัน)
ติดกับเนื้อหานั้นๆ และจะแสดงผลความหมายเมื่อเอาเมาส์ไปวางเหนือคำหนึ่งๆ
ช่วยให้สามารถเข้าใจเนื้อหาของเวบภาษาต่างประเทศได้สะดวกและรวดเร็วยิ่งขึ้น
ความหมายของคำจะปรากฏขึ้นมาเมื่อท่านเอาเมาส์ไปวางบนคำหรือวลีที่มีอยู่ในพจนานุกรม
โดยไม่จำเป็นต้องกดปุ่มใดๆ
ดังตัวอย่างในรูปข้างล่างนี้
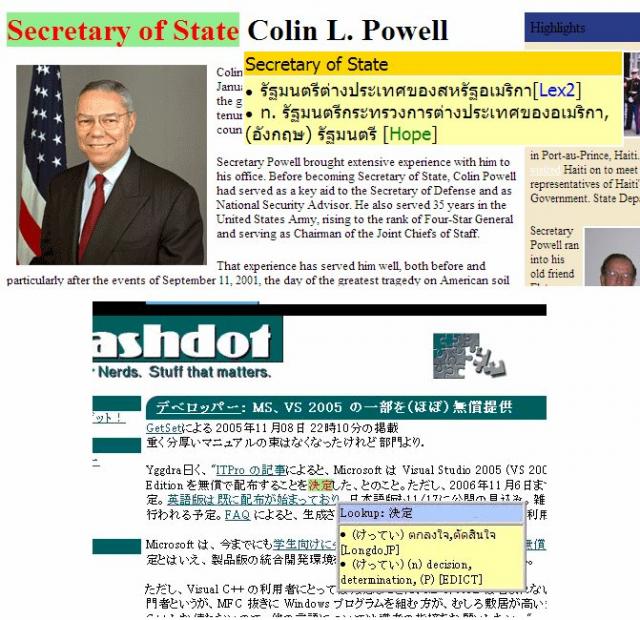
คุณสมบัติ / Features
- แสดงความหมายของคำโดยอัตโนมัติ เพียงวางเมาส์ไว้บนคำที่ต้องการทราบความหมาย
- สนับสนุนเวบหลากภาษา (ปัจจุบัน ภาษาอังกฤษ ญี่ปุ่น และเยอรมัน)
- ค้นหาความหมายจากพจนานุกรมหลายชุดพร้อมๆกัน ในฐานข้อมูลของ Longdo ได้แก่
Lexitron2, Hope, Nontri, Longdo อังกฤษ-ไทย, Longdo เยอรมัน-ไทย เป็นต้น - แสดงได้ทั้งความหมายของคำเดี่ยว และคำผสม ได้อย่างถูกต้อง
เช่น Secretary of State=รัฐมนตรีต่างประเทศของสหรัฐฯ (ในภาพตัวอย่าง),
High school=โรงเรียนมัธยมปลาย - แสดงความหมายของคำที่แปรรูปจากคำในพจนานุกรมได้ เช่น
เมื่อวางเมาส์ไว้บนคำว่า executed/abusing ซึ่งไม่มีในพจนานุกรม
เครื่องจะแสดงความหมายของคำว่า execute/abuse ให้โดยอัตโนมัติ - เรียกใช้งานได้ง่ายเพียงกดปุ่ม PopThai บน
Longdo Toolbar
เพื่อแนบความหมายหน้าจอที่เปิดชมอยู่ในขณะนั้น - แก้ไข Link ในหน้าที่แสดง เพื่อให้สามารถเปิดชม Link เหล่านั้นผ่านบริการ PopThai
ได้ทันทีเช่นเดียวกัน - สนับสนุนบราวเซอร์ชั้นนำทั่วไป เช่น Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Safari, Konqueror, etc.
- แสดง Link ให้ผู้ใช้ช่วยป้อนความหมายสำหรับคำที่ยังไม่มีอยู่ในพจนานุกรม
- ใหม่: บริการ Vocabulary แสดงสรุปรายการคำศัพท์พร้อมความหมาย สำหรับพิมพ์ออกมาอ่านได้สะดวก
วิธีใช้งาน ให้เลือกตรงตัวเลือกบริการด้านบน ให้เป็น Vocabulary แทน PopThai. (PopThai ในโหมดปกติ จะเหมาะกับการใช้งาน on-line
หน้าจอคอมพิวเตอร็ ส่วนบริการ Vocabulary เหมาะสำหรับท่านที่ต้องการพิมพ์รายการคำศัพท์และความหมายออกมาบนกระดาษไว้อ่าน off-line) - ใหม่: บริการ Pronunciation Guide แสดงคำอ่านของคำใน เว็บ หรือ text ที่ป้อนให้ ข้างบนคำนั้นๆ, นอกเหนือไป
จากการแสดง pop-up ความหมาย. วิธีใช้งาน ให้เลือกตรงตัวเลือกบริการด้านบน ให้เป็น Pronunciation.
ขณะนี้ใช้ได้กับภาษาอังกฤษ (แสดงคำอ่านภาษาอังกฤษ) และภาษาญี่ปุ่น (แสดง hiragana เหนือคันจิ). บริการนี้
ใช้ extension ของ browser ที่ชื่อ Ruby ปัจจุบันมีแค่ IE browser ที่สนับสนุน ถ้าเป็น browser อื่นๆ จะเห็นคำอ่านปรากฎในวงเล็บแทน
วิธีใช้
ท่านสามารถป้อนเนื้อหาหรือ URL ของเว็บไซต์ที่ต้องการให้แนบความหมายนี้ ในช่องใส่ข้อความค้นหาปกติ
หลังจากนั้นเลือกบริการที่ต้องการ (เช่น ถ้าป้อนข้อความ ให้เลือก PopThai (text) ถ้าป้อน URL ให้เลือก PopThai (URL)) ถ้าท่านไม่เลือกบริการ
ระบบจะเดาบริการที่ท่านต้องการ จากข้อความที่ท่านใส่เข้ามา (ว่าเป็นข้อความหรือเป็น URL) โดยอัตโนมัติ,
จากนั้นกด Submit เป็นอันเสร็จ
ในกรณีที่ท่านใส่ URL ระบบจะไปทำการดาวน์โหลดเนื้อหาของหน้านั้นๆ มาและแนบความหมาย พร้อมแก้ไขลิงค์ต่างๆ ให้เป็นผ่านบริการ PopThai เ
พื่อที่ว่าเมื่อท่านกดที่ลิงค์ใดๆ ต่อไปจากเพจนั้นๆ ก็จะมีการแนบความหมายมาให้ด้วยในทันที
เพื่อเพิ่มความสะดวกในการใช้ท่านสามารถใช้ PopThai ผ่าน Longdo Toolbar โดยเมื่อท่านเปิดดูเว็บไซต์ใดๆ อยู่ตามปกติ และต้องการใช้บริการ PopThai สำหรับ
หน้านั้นๆ สามารถทำได้ทันที โดยคลิกที่ปุ่ม PopThai บน Toolbar รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมโปรดอ่านที่ Longdo Toolbar
คำเตือน ในกรณีของ URL นี้ ถึงแม้ทางผู้ดูแลระบบลองดูจะได้ทำการทดสอบกับหลายเว็บไซต์
แล้วก็ตาม ยังมีบางเว็บไซต์ที่ข้อมูลเวลาที่ระบบไปโหลดมาจะแตกต่างจากที่ท่านเปิดดูโดยใช้ browser โดยตรง โปรดระวังด้วย และไม่ควรใช้กับหน้าเว็บไซต์ที่
ต้องการความถูกต้องสูง)
Problems & TODO
- inflected word support (German)
- support HTTP POST
- other foreign language support (Japanese, French)
\”ซื้อรถหมดห่วง รับรองโดยGoo Inspection\”
\”ซื้อรถหมดห่วง รับรองโดยGoo Inspection\”
มั่นใจด้วยมาตรฐานการตรวจรถจากประเทศญี่ปุ่น ดูรถไม่เป็นก็ซื้อได้ เพราะมีใบรับประกันโครงสร้างตัวถังเดิมไม่มีชนหนัก พลิกคว่ำ จมน้ำ
🎉บริการเซ็นต์ไฟแนนซ์ที่ ส่งรถสวยถึงหน้าบ้าน
.
📲สนใจโทร 0875097878
แอดไลน์ : @admirecar (มี@ด้านหน้า)
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูเพิ่มเติม

วิชา Statics เรื่อง การหาจุดศูนย์กลางมวลเป็นวิธีการหา Centroid
วิชา Statics เรื่อง การหาจุดศูนย์กลางมวล
รายละเอียดบทเรียน: เป็นวิธีการหา Centroid หรือ Center of Mass ของวัตถุที่ประกอบจากรูปเลขคณิต เช่น สามเหลี่ยม สี่เหลี่ยม วงกลม เป็นต้น
เอกสาร: https://www.scribd.com/document/499393145/
[รายละเอียดคอร์สออนไลน์]
• เรียนแบบออนไลน์ 100%
• สามารถดูซ้ำได้ไม่จำกัด
• สงสัยตรงไหนก็ทัก line ส่วนตัวมาถามพวกพี่ได้โดยตรง
• ฟรีหนังสือประกอบการเรียน ที่รวบรวมจาก textbook กว่า 3 เล่ม (จัดส่งฟรีถึงบ้าน)
• อัดแน่นด้วยโจทย์ พร้อมเฉลยอย่างละเอียดทุกข้อ
• สอนโดยติวเตอร์เกียรตินิยม ประสบการณ์สอนกว่า 10 ปีทุกคน
[สมัครเรียน/สอบถามรายละเอียด]
• Line: @beengineer
• โทร : 0824902232 (พี่อิ้ว), 0869405548 (พี่จุ๊)
• FB: https://www.facebook.com/beengineer2012/
• สาขา ลาดกระบัง www.facebook.com/be.engineer.kmitl

วิชาฟิสิกส์ – บทเรียน จุดศูนย์กลางมวลและจุดศูนย์ถ่วง
วิชาฟิสิกส์ บทเรียน จุดศูนย์กลางมวลและจุดศูนย์ถ่วง
สื่อการสอนภายในโครงการจัดทำสื่อการสอน วิทยาศาสตร์และคณิตศาสตร์ ระดับมัธยมศึกษาตอนปลาย
โดย ความร่วมมือระว่าง สำนักงานคณะกรรมการการศึกษาขั้นพื้นฐาน กระทรวงศึกษาธิการ และ คณะวิทยาศาสตร์ จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย
สื่อการสอนชุดนี้จัดทำขึ้นเพื่อการศึกษาของประเทศ ห้ามมิให้นำไปใช้ในเชิงพาณิชย์โดยเด็ดขาด หากผู้ใดฝ่าฝืนจะดำเนินการทางกฎหมายโดยทันที
ติดตามได้ที่
website http://www.scicoursewarechula.com/
facebook https://www.facebook.com/pages/SciCoursewareThai/179595712245778?fref=ts

4.2 จุดศูนย์กลางมวลและจุดศูนย์ถ่วง (ฟิสิกส์เพิ่มเติม ม. 4 บทที่ 4)

8.4 ศูนย์กลางมวลและศูนย์ถ่วง
เล่ม : ฟิสิกส์ เพิ่มเติม ม.46 เล่ม2
บท : สภาพสมดุลและสภาพยืดหยุ่น
Playlist : https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLrEFzH81p36hpz9H_88koNTbMuvr5OiZj

นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูบทความเพิ่มเติมในหมวดหมู่Wiki
ขอบคุณมากสำหรับการดูหัวข้อโพสต์ จุดศูนย์ถ่วง